In January 2006, podcasts surged in popularity worldwide. Today, they’re experiencing a resurgence.
What does this resurgence entail? It’s quite simple. Think about where you typically listen to music when you’re on the move. In a fast-paced world where we’re always on the move, we crave moments of relaxation. However, platforms like YouTube still require active screen engagement, preventing us from multitasking. But with services such as SoundCloud, Mixcloud, Spotify, and others, we can listen to music or audiobooks in the background while accomplishing other tasks.
Unlike YouTube, which is primarily restricted to home viewing, SoundCloud, Mixcloud, and Spotify cater to our mobile lifestyles. Our smartphones have become multitasking marvels, although the practice of multitasking isn’t necessarily ideal (a point I’ll delve into later). Given that many of us spend significant time commuting by car, public transport, bicycle, or other means, we often opt to listen rather than watch, plugging in our earbuds and immersing ourselves in audio content.
This shift in consumer behavior is why I believe podcasts are making a comeback. Much of our time is spent listening rather than watching due to our constant mobility.
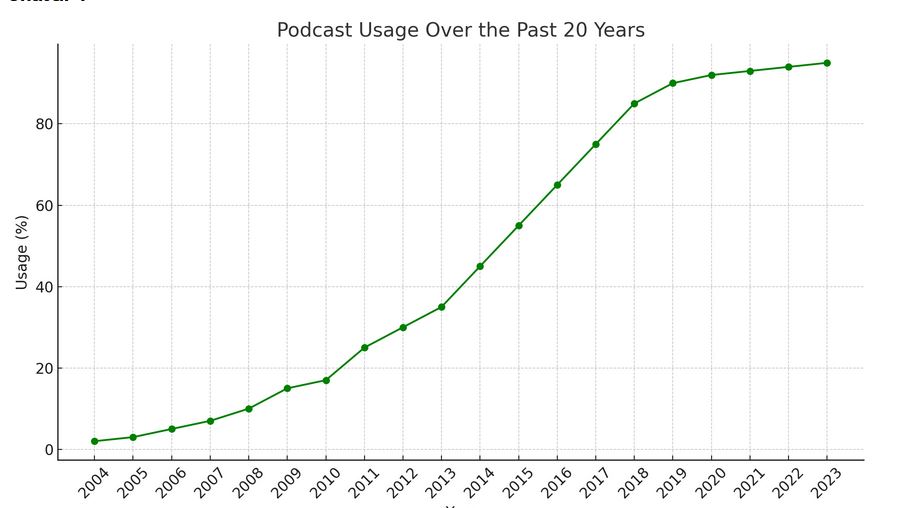
The EU’s podcast market has been experiencing a steady growth, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behavior, and the increased production of localized content.
1. Growth in audience size
- Increasing listenership: There has been a significant increase in the number of people listening to podcasts across various EU countries. This is attributed to the ease of access to digital platforms and the growing penetration of smartphones and smart speakers.
- Diverse demographics: Podcast listeners in the EU are diverse, spanning different age groups, with a notable inclination towards younger audiences who favor digital media over traditional.
2. Content localization and diversity
- Localized content: One of the strengths of the EU podcast scene is the emphasis on local languages and culturally relevant content. Countries such as France, Germany, Spain, and Italy have seen a surge in podcasts that cater to local interests, history, and entertainment, which has helped in attracting a wider audience.
- Genre expansion: While initially dominated by genres like tech, education, and news, the EU podcast market now includes a wide array of topics such as true crime, comedy, health, and lifestyle, reflecting global trends.
3. Technological advancements
- Platform growth: The proliferation of podcast platforms, including Spotify, Apple Podcasts, and local EU-based platforms, has made podcasts more accessible to the EU audience. These platforms often feature personalized recommendations, further enhancing listener engagement.
- Integration with smart devices: The integration of podcasts into smart devices and vehicles has facilitated seamless access for listeners, contributing to the growth in podcast consumption during commutes and leisure times.
4. Regulatory environment and funding
- Support for creators: Some EU countries have introduced initiatives and funding opportunities for podcast creators, recognizing the cultural and educational value of podcasts. This support has spurred innovation and quality in podcast production.
- Regulation and privacy: The EU’s regulatory stance on digital privacy and data protection affects how podcast platforms operate and interact with listeners, emphasizing transparency and consent in data usage.
5. Challenges and opportunities
- Monetization: While there are increasing opportunities for monetization through advertising, sponsorships, and subscription models, finding a sustainable business model remains a challenge for some podcast creators in the EU.
- International competition: EU podcasters face competition from English-language content, which has a broader global audience. However, this also presents an opportunity for niche and localized content to attract dedicated listenerships.
